Transform Your Deployment Process With AWS Automation
“Did you know that pushing code to GitHub can trigger automatic deployments through AWS without manual intervention?”
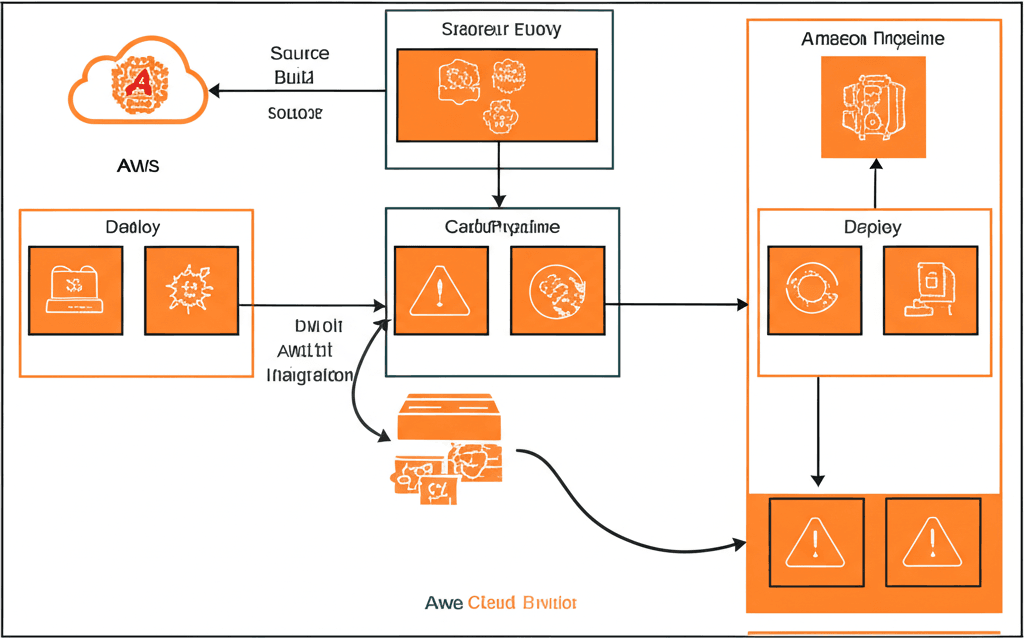
This comprehensive guide will walk you through creating a complete CI/CD pipeline on Amazon Web Services (AWS) using CodePipeline integrated with GitHub, providing a streamlined approach for developers to automate their software delivery process.
Understanding CI/CD Fundamentals
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) form the backbone of modern DevOps practices:
- Continuous Integration: Automatically testing and packaging code changes whenever developers push to version control
- Continuous Deployment: Automatically releasing validated code to production environments without human intervention
Implementing this system acts like hiring an automated DevOps engineer who manages your build, test, and deployment processes 24/7.
Core AWS Architecture Components
| Component | Function | Integration Point |
|---|---|---|
| GitHub Repository | Source code version control | Pipeline trigger source |
| AWS CodePipeline | Orchestration workflow management | Central coordination hub |
| AWS CodeBuild | Automated testing & packaging | Optional build stage |
| AWS Deployment Services | Serverless/container/instance targets | Final deployment destination |
Essential Prerequisites
Before building your automation pipeline:
- Create or identify a GitHub repository containing your application codebase
- Establish an AWS account with appropriate IAM permissions
- Understand basic Git commands and workflows
- Determine your deployment target (S3 bucket, EC2 instance, ECS cluster, etc.)
Building Your Automated Pipeline: Step-by-Step Implementation
1. GitHub/AWS Integration Setup
- Navigate to AWS Management Console → CodePipeline service
- Select “Create Pipeline” and configure pipeline name/region
- Under Source Provider: Select “GitHub (version 2)”
- Authenticate and connect your GitHub account using OAuth
- Choose target repository and branch (main/master recommended)
2. CodeBuild Configuration (Optional Build Stage)
For projects requiring compilation or testing:
- Add Build stage to your pipeline workflow
- Select “AWS CodeBuild” as build provider
- Create new build project or select existing configuration
- Implement buildspec.yml configuration file:
version: 0.2
phases:
install:
runtime-versions:
nodejs: 18
build:
commands:
- npm install
- npm run build
- npm test
artifacts:
files:
- '**/*'
3. Deployment Target Configuration
- Amazon S3: Static website hosting for frontend applications
- EC2/On-Premises: Use CodeDeploy for instance-based deployments
- AWS Lambda: Serverless function updates via SAM/Serverless Framework
- Amazon ECS: Containerized application deployments
Advanced Configuration Options
- Manual Approval Gates: Add human verification points before production releases
- Parallel Workflows: Implement multi-region deployments using pipeline branching
- Pipeline Triggers: Configure webhooks for custom event-based execution
- Test Automation: Integrate end-to-end testing suites in staging environments
Why Automate Your Deployment Process?
- 🚀 Accelerated Release Cycles: Reduce deployment time from hours to minutes
- 🛡️ Consistent Environments: Eliminate configuration drift between development/staging/production
- 🔍 Early Error Detection: Automatic testing identifies issues before production impact
- 📈 Scalability: Handle increased deployment frequency without proportional resource increase
- 💸 Cost Reduction: Minimize manual deployment efforts and associated labor costs
Troubleshooting Common Pipeline Issues
- Connection Failures: Verify GitHub OAuth token validity and repository permissions
- Build Timeouts: Adjust CodeBuild timeout settings for complex compilation processes
- Deployment Rollbacks: Configure automatic rollback triggers for failed deployments
- Permission Errors: Review IAM roles for CodePipeline service permissions
Optimization Best Practices
- Implement pipeline caching to accelerate build times
- Use parallel test execution in CodeBuild phase
- Set up CloudWatch monitoring for pipeline performance metrics
- Implement security scans using Amazon Inspector during build process
- Configure notifications through Amazon SNS for pipeline events
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I deploy to non-AWS environments using this pipeline?
A: Yes, CodePipeline supports hybrid deployments through custom actions and on-premises agents.
Q: Does this work with private GitHub repositories?
A: Absolutely – the OAuth connection handles both public and private repositories.
Q: What’s the cost structure for using CodePipeline?
A: AWS CodePipeline pricing is based on active pipelines and monthly executor minutes, with a free tier available for new users.
Q: Can I integrate third-party tools like Slack notifications?
A: Yes, through Lambda actions and SNS integrations for custom notifications.
Next Steps in Your Automation Journey
Once your basic CI/CD pipeline is operational, consider expanding your automation capabilities with:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using AWS CloudFormation
- Automated database migration management
- Advanced monitoring with AWS X-Ray and CloudWatch
- Security scanning integration in the build process
By implementing this automated CI/CD workflow, you’ll transform your development process into a streamlined, efficient system that reduces errors and accelerates your time-to-market for new features and updates.
Leave a Reply